
 CM 1000 NDVI计
CM 1000 NDVI计
 色彩色差计——CR-400/CR-410
色彩色差计——CR-400/CR-410
 植物多酚-叶绿素测量计——Dualex Scientific+
植物多酚-叶绿素测量计——Dualex Scientific+
 CM 1000叶绿素计
CM 1000叶绿素计
 便携式叶绿素仪——SPAD-502 Plus
便携式叶绿素仪——SPAD-502 Plus
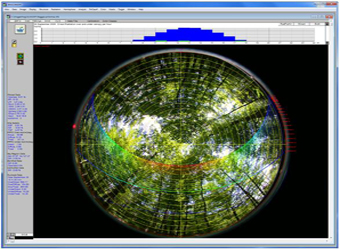
主要功能 使用 180 度鱼眼镜头和高清晰度数码相机从植物冠层下方或森林地面向上获取植物冠层图像,然后通过处理影像数据文件来获取与冠层结构有关的叶面积指数、光照间隙及间隙分布状况等参数。 通过分析辐射数据的相关信息,WinSCANOPY 能够测算出冠层截获的 PAR 以及冠层下方的辐射水平。其软件可以计算辐射指标、冠层指标、测量地点的光线覆盖状况及直射与漫射光的分布。 Mask 功能:View caps 屏蔽某一影像区域, 以便对特定的区域中作出有效的直接分析。 可在 0-360 度转角和方向内任意设定。 图表分析功能:直接辐射、 漫辐射、 总辐射变化;一天内每个小时内的冠层上下的辐射变化;季节内特定天内的每天辐射变化;GAP 随每个提升高度或方向上,以及LAI叶面积指数的变化。
| |
测量参数 冠层结构测量参数:透光面积,间隙指数,叶面积指数(LAI),叶倾角分布(LAD) ,平均叶倾角(MLA),叶片投影系数,单株叶密度,丛生指数,单株 LAI,分析单独叶面积和土壤覆盖层非半球图片,个别冠层分析,间隙大小分配,全画面鱼眼图像分析。 辐射测量参数:散射因子,林冠上方和下方直接辐射和散射,特殊时期的直接辐射及总辐射部分,直射、散射、总辐射因子,林冠下直射时间比率,地面坡度,每日光斑分布。 | |
应用领域 广泛应用于园艺、农业、林业植物冠层研究。 |  |
| |
| |
| |
主要技术参数 特点
| |
测量参数
| |
选购指南
产地:加拿大 Regent | |
参考文献 原始数据来源:Google Scholar Xi B, Bloomberg M, Watt MS, Wang Y, Jia L (2016) Modeling growth response to soil water availability simulated by HYDRUS for a mature triploid Populus tomentosa plantation located on the North China Plain. Agricultural Water Management 176: 243-254. Woods NN, Miriti MN (2016) Ubiquitous germination among common perennial species in response to facilitated and unfacilitated microhabitats. Journal of Arid Environments 124: 72-79. Wang T, Kang F, Cheng X, Han H, Ji W (2016) Soil organic carbon and total nitrogen stocks under different land uses in a hilly ecological restoration area of North China. Soil and Tillage Research 163: 176-184. Strauch AM, Bruland GL, MacKenzie RA, Giardina CP (2016) Soil and hydrological responses to wild pig (Sus scofa) exclusion from native and strawberry guava (Psidium cattleianum)-invaded tropical montane wet forests. Geoderma 279: 53-60. Rejžek M, Svátek M, Šebesta J, Adolt R, Maděra P, et al. (2016) Loss of a single tree species will lead to an overall decline in plant diversity: Effect of Dracaena cinnabari Balf. f. on the vegetation of Socotra Island. Biological Conservation 196: 165-172. Feltrin RP, Will RE, Meek CR, Masters RE, Waymire J, et al. (2016) Relationship between photosynthetically active radiation and understory productivity across a forest-savanna continuum. Forest Ecology and Management 374: 51-60. Chianucci F, Disperati L, Guzzi D, Bianchini D, Nardino V, et al. (2016) Estimation of canopy attributes in beech forests using true colour digital images from a small fixed-wing UAV. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation 47: 60-68. Chen D, Wang Y, Wang X, Nie Z, Gao Z, et al. (2016) Effects of branch removal on water use of rain-fed jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.) plantations in Chinese semiarid Loess Plateau region. Agricultural Water Management 178: 258-270. Winter M-B, Ammer C, Baier R, Donato DC, Seibold S, et al. (2015) Multi-taxon alpha diversity following bark beetle disturbance: Evaluating multi-decade persistence of a diverse early-seral phase. Forest Ecology and Management 338: 32-45. Shabaga JA, Basiliko N, Caspersen JP, Jones TA (2015) Seasonal controls on patterns of soil respiration and temperature sensitivity in a northern mixed deciduous forest following partial-harvesting. Forest Ecology and Management 348: 208-219. Sebek P, Bace R, Bartos M, Benes J, Chlumska Z, et al. (2015) Does a minimal intervention approach threaten the biodiversity of protected areas? A multi-taxa short-term response to intervention in temperate oak-dominated forests. Forest Ecology and Management 358: 80-89. Samperio A, Prieto MH, Blanco-Cipollone F, Vivas A, Moñino MJ (2015) Effects of post-harvest deficit irrigation in ‘Red Beaut’ Japanese plum: Tree water status, vegetative growth, fruit yield, quality and economic return. Agricultural Water Management 150: 92-102. Samperio A, Moñino MJ, Vivas A, Blanco-Cipollone F, Martín AG, et al. (2015) Effect of deficit irrigation during stage II and post-harvest on tree water status, vegetative growth, yield and economic assessment in ‘Angeleno’ Japanese plum. Agricultural Water Management 158: 69-81. Moser A, Rötzer T, Pauleit S, Pretzsch H (2015) Structure and ecosystem services of small-leaved lime (Tilia cordata Mill.) and black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia L.) in urban environments. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening 14: 1110-1121. Hanula JL, Horn S, O’Brien JJ (2015) Have changing forests conditions contributed to pollinator decline in the southeastern United States? Forest Ecology and Management 348: 142-152. Crosby AD, Elmore RD, Leslie Jr DM, Will RE (2015) Looking beyond rare species as umbrella species: Northern Bobwhites (Colinus virginianus) and conservation of grassland and shrubland birds. Biological Conservation 186: 233-240. Coonen EJ, Sillett SC (2015) Separating effects of crown structure and competition for light on trunk growth of Sequoia sempervirens. Forest Ecology and Management 358: 26-40. Chen D, Wang X, Liu S, Wang Y, Gao Z, et al. (2015) Using Bayesian analysis to compare the performance of three evapotranspiration models for rainfed jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.) plantations in the Loess Plateau. Agricultural Water Management 159: 341-357. Cavallero L, López DR, Raffaele E, Aizen MA (2015) Structural–functional approach to identify post-disturbance recovery indicators in forests from northwestern Patagonia: A tool to prevent state transitions. Ecological Indicators 52: 85-95. Capdevielle-Vargas R, Estrella N, Menzel A (2015) Multiple-year assessment of phenological plasticity within a beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) stand in southern Germany. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology 211–212: 13-22.
| |

报价:面议
已咨询133次植物保护研究
报价:面议
已咨询472次植物光谱与冠层测量

报价:¥1
已咨询316次植物生理仪器

报价:面议
已咨询216次植物冠层分析仪

报价:面议
已咨询342次植物光谱与冠层测量

报价:面议
已咨询73次植物冠层分析仪

报价:面议
已咨询52次生命科学仪器

报价:面议
已咨询370次植物表型成像分析技术

组培是指在人工培养基上,离体培养植物的器官、组织、细胞和原生质体,并使其生长、增殖、分化以及再生植株的新型科学技术。其实植物体的每一个细胞都携带有一套完整的基因组,并具有发育成完整植株的潜在能力。

Viscon的自动化种子加工解决方案,可简化多种大田作物种子的自动化采样与 DNA 分析制备流程。通过自动化处理单粒种子,确保基因分型制备的精准性,同时维持质量控制标准。

SciSpinner Max 3D是一款专为生命科学、生物制药、材料科学、植物科学等实验室打造的双轴3D回旋器,以双轴独立旋转技术为核心,360°无死角抵消重力矢量,提供贴近太空的无重力干扰环境。高性价比打通基础科研与工业应用,适配从样品培养到机制研究的全场景需求。

协作运维机器人由机器人本体、工业机械臂以及手持智能遥控终端组成。主要应用领域是特高压电站运维领域,为运维人员提供快速、准确的变电站设备动态,解决由于人员专业水平差异而导致变电站巡检质量不足的问题,相较于传统的人工巡检操作,能够显著降低大量人力与时间成本,较大程度地解决“人站比”不足的问题,使得环境日益凸显的矛盾得以缓解。

光伏运维机器人由机器人本体、升降云台、可翻转除草模块和手持智能遥控终端组成。主要用于集中式光伏电站的运维领域,取代运维人员进行光伏板巡检、除草等重复性任务。

基于“AI+"计划,“山猫”在具身智能方面的技术积累的同时,基于”山猫“的形态针对性进行特色化适配。

户外巡检与救援侦查中,不同季节与地区的温差巨大,作为行业级旗舰机型,SpecBotics-30工作温度范围大幅提升,已在-20℃至55℃的应用环境中经过实战检验,且拥有严格检测的IP67防护等级

DUALEX是一款便携式叶片测量仪,能够精确测量叶片表面的叶绿素含量(ug/cm²)和类黄酮指数。在植物科学领域被广泛应用于研究植物对环境应激因子的响应、养分管理以及生理学研究。DUALEX还可计算氮平衡指数(NBl),该指数已被证明与叶片氮素含量密切相关。